
ユビキチン様分子ISG15依存性タンパク質翻訳制御と自然免疫応答の関連性の解析
 |
研究代表者 奥村文彦 名古屋大学・理学系・助教 http://bunshi4.bio.nagoya-u.ac.jp/~2kamura/ |
【研究概要】
1979年にISG15はインターフェロン刺激で誘導されるユビキチン様分子として発見された。(Farrell et al. 1979) その後約30年経過したがISG15に対する研究はほとんど進んでいないのが現状である。ISG15のタンパク質発現は厳しく制御されており、通常の状態では細胞内に発現していないがインターフェロン(IFN)やウイルス感染、大腸菌構成成分であるリポ多糖体(LPS)などの刺激により急速に発現誘導されることが知られている。ISG15修飾に必要な酵素群(UBE1L, E2, E3)さらには脱ISG15酵素UBP43も同様の刺激で発現が誘導される(図1)。したがって、初期免疫システム(特に自然免疫)に関与すると長年信じられているが、それを証明する詳細な分子メカニズムは未だ発見されていない。しかしながらISG15欠損マウスを用いた研究によりISG15修飾は特定のウイルス(インフルエンザやヘルペスウイルスなど)に対する抗ウイルス活性があることが報告され、免疫制御に関与することが示されている 。(Lenschow et al. 2007)
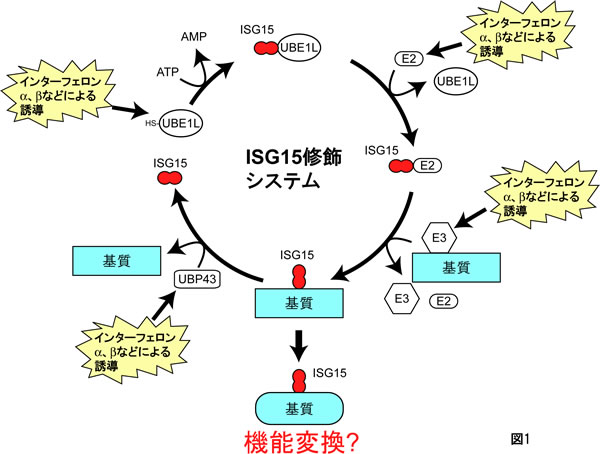
図2に示すようにISG15は150種類を超える基質タンパク質の翻訳後修飾に用いられることが分かっている。(Giannakopoulos et al. 2005; Zhao et al. 2005; Takeuchi et al. 2006)
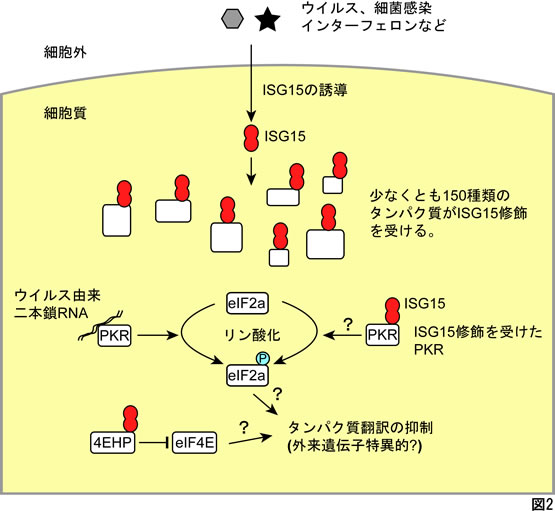
本研究では私達が初めて同定した、ISG15修飾による基質分子の「gain-of-function」の生理的役割をさらに明らかにすることを目的とする。すなわち、メッセンジャーRNAのキャップ構造結合分子4EHPはISG15修飾を受けると未修飾のものよりも10-20倍強いキャップ構造結合活性を獲得し、ある特定のメッセンジャーRNAのタンパク質翻訳を選択的に阻害することを見出したので、生理的環境下における標的遺伝子を同定し、ISG15修飾の生理的役割を明らかにすることを目的とする。(Okumura et al. 2007; Okumura et al. 2008)
また、ISG15同様にインターフェロン刺激で発現誘導されるリン酸化酵素PKRはウイルス由来の二本鎖RNAと結合することで活性化する。PKRがISG15修飾を受けることを見出したので、ISG15修飾によって酵素活性がどのように変化するかを明らかにする。
【参考文献】
- Farrell, P.J., R.J. Broeze, and P. Lengyel. 1979. Accumulation of an mRNA and protein in interferon-treated Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Nature 279: 523-5.
- Giannakopoulos, N.V., J.K. Luo, V. Papov, W. Zou, D.J. Lenschow, B.S. Jacobs, E.C. Borden, J. Li, H.W. Virgin, and D.E. Zhang. 2005. Proteomic identification of proteins conjugated to ISG15 in mouse and human cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336: 496-506.
- Lenschow, D.J., C. Lai, N. Frias-Staheli, N.V. Giannakopoulos, A. Lutz, T. Wolff, A. Osiak, B. Levine, R.E. Schmidt, A. Garcia-Sastre, D.A. Leib, A. Pekosz, K.P. Knobeloch, I. Horak, and H.W.t. Virgin. 2007. IFN-stimulated gene 15 functions as a critical antiviral molecule against influenza, herpes, and Sindbis viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 1371-6.
- Okumura, F., D.J. Lenschow, and D.E. Zhang. 2008. Nitrosylation of ISG15 prevents the disulfide bond-mediated dimerization of ISG15 and contributes to effective ISGylation. J Biol Chem 283: 24484-8.
- Okumura, F., W. Zou, and D.E. Zhang. 2007. ISG15 modification of the eIF4E cognate 4EHP enhances cap structure-binding activity of 4EHP. Genes Dev 21: 255-60.
- Takeuchi, T., S. Inoue, and H. Yokosawa. 2006. Identification and Herc5-mediated ISGylation of novel target proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348: 473-7.
- Zhao, C., C. Denison, J.M. Huibregtse, S. Gygi, and R.M. Krug. 2005. Human ISG15 conjugation targets both IFN-induced and constitutively expressed proteins functioning in diverse cellular pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 10200-5.











